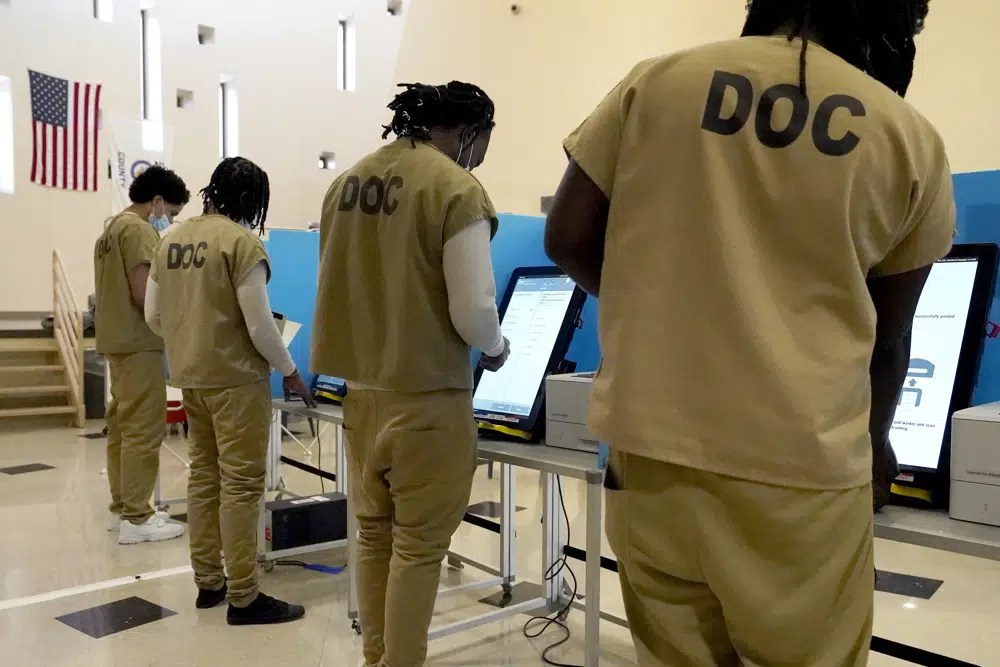
CHICAGO (AP) — The voting precinct could have been any one of hundreds throughout Chicago, except that these voters in the first round of the mayoral election were all wearing the same beige smocks. And the security at this polling place wasn’t intended to keep disrupters and campaigners out, but the voters in.
When first-time voter Tykarri Skillon finished studying the list of nine candidates, looking for those who shared his priorities on jobs and affordable housing, he marked his ballot and then was escorted with other voters back to their cells in the Cook County Jail.
The 25-year-old, awaiting trial on a weapons charge, is part of a group not always mentioned in discussions about voting disenfranchisement. People serving sentences for felony convictions lose their right to vote. Detainees awaiting trial or serving misdemeanor sentences do retain that right, but face barriers to exercising it in many parts of the United States.
The Cook County Jail, with more than 5,500 inmates and detainees, is one of the largest such facilities in the nation. It is one of several lockups where voting rights advocates have worked with local election and jail officials to offer voting for those held there. The list includes jails in Denver; Harris County, Texas; Los Angeles County; and the District of Columbia.
Expanding jailhouse voting is one of the latest steps to combine voting rights with criminal justice changes.
“It feels good to have a voice,” Skillon said after casting his ballot during early voting, before the race went to an April 4 runoff. “We’re going home someday, so we should have a voice in our community.”
Candidates he chose from included the current mayor, Democrat Lori Lightfoot. Among the issues that damaged her politically was rising crime. She eventually came in third in the election, bumping her from an April 4 runoff between the two top vote-getters, also…
Read the full article here