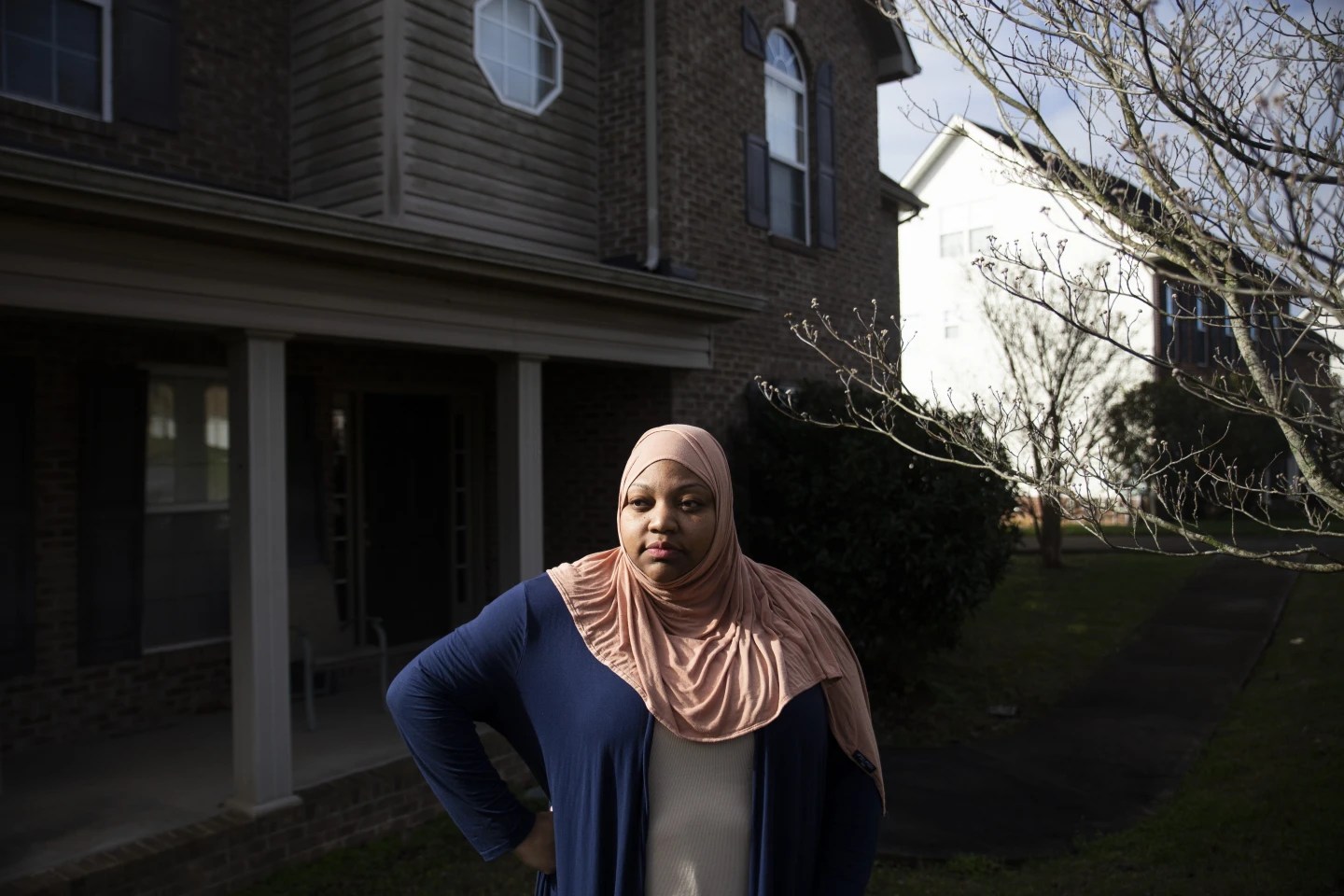WASHINGTON (AP) — As Salvatore LoGrande fought cancer and all the pain that came with it, his daughters promised to keep him in the white, pitched roof house he worked so hard to buy all those decades ago.
So, Sandy LoGrande thought it was a mistake when, a year after her father’s death, Massachusetts billed her $177,000 for her father’s Medicaid expenses and threatened to sue for his home if she didn’t pay up quickly.
“The home was everything,” to her father said LoGrande, 57.
But the bill and accompanying threat weren’t a mistake.
Rather, it was part of a routine process the federal government requires of every state: to recover money from the assets of dead people who, in their final years, relied on Medicaid, the taxpayer-funded health insurance for the poorest Americans.
A person’s home is typically exempt from qualifying for Medicaid. But it is subject to the estate recovery process for those who were over 55 and used Medicaid to pay for long-term care such as nursing home stays or in-home health care.
This month, a Democratic lawmaker proposed scuttling the “cruel” program altogether. Critics argue the program collects too little — roughly 1% — of the more than $150 billion Medicaid spends yearly on long-term care. They also say many states fail to warn people who sign up for Medicaid that big bills and claims to their property might await their families once they die.
LoGrande says that’s how she ended up in a two-year legal battle with Massachusetts after her father died. Several years before he died in 2016, she had turned to a local nonprofit for advice on caring for her elderly father. The group suggested she sign him up for Medicaid. She even remembers asking about the house, but was assured the state would only seek the house if it sent her father to a nursing home.
“He never would have signed on with anything that would put his home in jeopardy,” she said.
For years,…
Read the full article here